
最新刊期
卷 39 , 期 4 , 2025
-
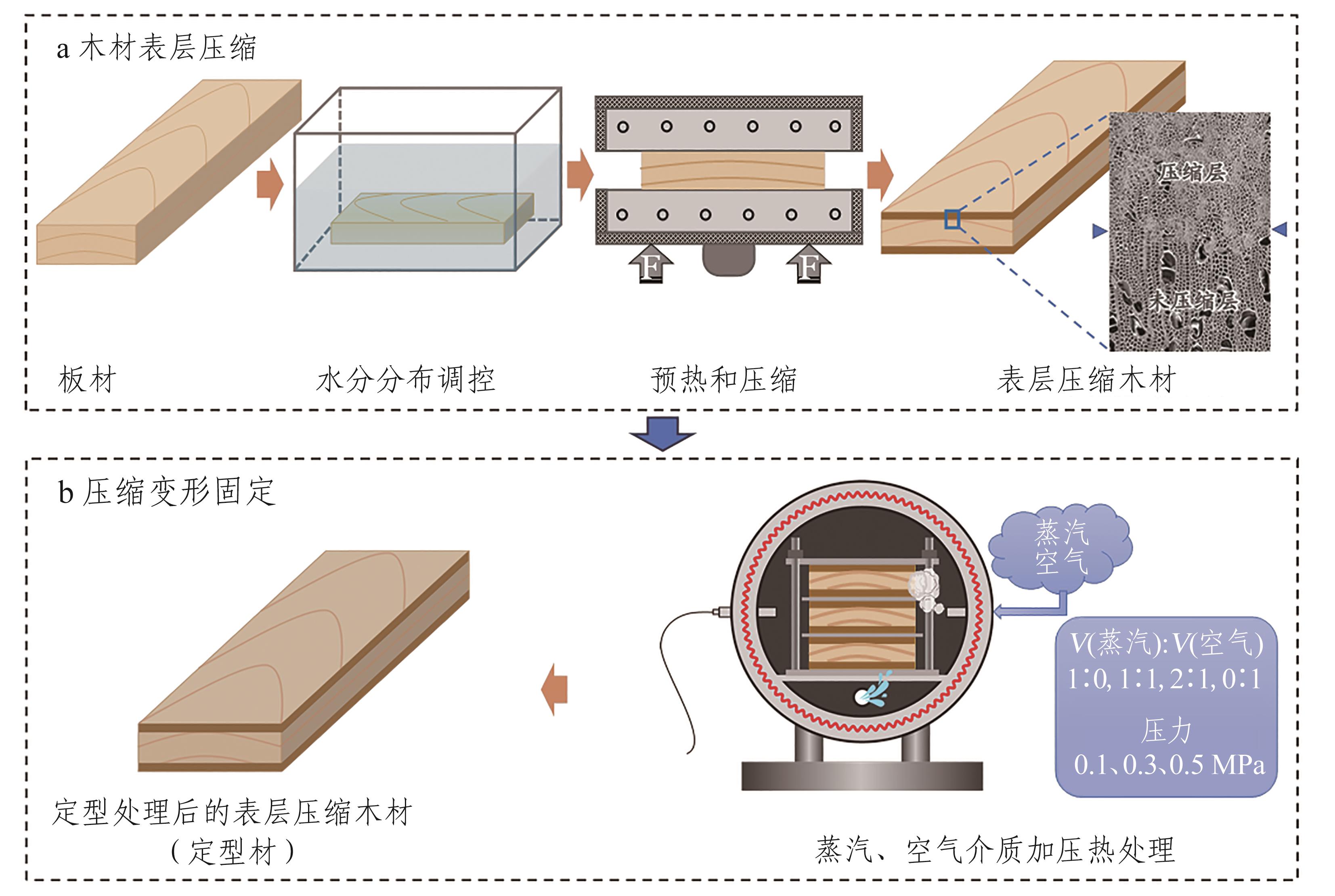 摘要:Permanent setting of compressive wood deformation has been a focus of wood modification. The heated and pressurized air only, steam only, and their mixture were applied as the heating media to treat surface-compressed poplar wood (Populus tomentosa) to study permanent setting. In the heat treatment process, the medium pressures were 0.1 MPa, 0.3 MPa, and 0.5 MPa; the treatment temperature was 180 ℃; the treatment time was 2 hours. The effects of treatments on the set recovery, physical, chemical, and mechanical properties of compressed wood were recorded and analyzed. When steam-only treatment was used, at 0.5 MPa, around 80% of the compression was permanently set, compared to 54% of the compression deformation setting when air-only treatment was used. Although air-only treatment causes hemicellulose degradation, by-products of acetic acid and aldehyde compounds were significantly lower than that when steam-only treatment was applied. The correlation between set recovery induced from water absorption and crystallinity index (r=0.921, p<0.01) was closer than that between set recovery induced from water absorption and hydroxyl absorption strength based on the statistical analysis of the entire sample (r=0.557, p<0.05). It partially explained that hemicellulose degradation process contributed to permanent setting, greater than hygroscopicity decreased due to the reduction of hydroxyl groups. Compared with air-only, when the volume ratio of air and steam was 1∶1 or with steam ratio in the medium, the reduction rate of EMC and set recovery on the treated wood increased by 50%, and the loss rate of wood hardness and surface hardness decreased by more than 4.6%. The mixture of air and steam reduced the amount of steam used in the treatment process and simplified the treatment process. This process significantly reduces the production cost of compressed wood and accelerates the commercial application of wood compression technology.关键词:white poplar;setting of compressive deformation;air medium;steam medium;set recovery;chemical components31|0|0更新时间:2025-09-11
摘要:Permanent setting of compressive wood deformation has been a focus of wood modification. The heated and pressurized air only, steam only, and their mixture were applied as the heating media to treat surface-compressed poplar wood (Populus tomentosa) to study permanent setting. In the heat treatment process, the medium pressures were 0.1 MPa, 0.3 MPa, and 0.5 MPa; the treatment temperature was 180 ℃; the treatment time was 2 hours. The effects of treatments on the set recovery, physical, chemical, and mechanical properties of compressed wood were recorded and analyzed. When steam-only treatment was used, at 0.5 MPa, around 80% of the compression was permanently set, compared to 54% of the compression deformation setting when air-only treatment was used. Although air-only treatment causes hemicellulose degradation, by-products of acetic acid and aldehyde compounds were significantly lower than that when steam-only treatment was applied. The correlation between set recovery induced from water absorption and crystallinity index (r=0.921, p<0.01) was closer than that between set recovery induced from water absorption and hydroxyl absorption strength based on the statistical analysis of the entire sample (r=0.557, p<0.05). It partially explained that hemicellulose degradation process contributed to permanent setting, greater than hygroscopicity decreased due to the reduction of hydroxyl groups. Compared with air-only, when the volume ratio of air and steam was 1∶1 or with steam ratio in the medium, the reduction rate of EMC and set recovery on the treated wood increased by 50%, and the loss rate of wood hardness and surface hardness decreased by more than 4.6%. The mixture of air and steam reduced the amount of steam used in the treatment process and simplified the treatment process. This process significantly reduces the production cost of compressed wood and accelerates the commercial application of wood compression technology.关键词:white poplar;setting of compressive deformation;air medium;steam medium;set recovery;chemical components31|0|0更新时间:2025-09-11 -
 摘要:Effects of heating media composition and its pressure on color changes in wood during permanent compression deformation were analyzed using statistical methods. The heating media, including steam only, air only, nitrogen (N2) only, and the mixture of either steam combining with air or steam combining with N2 were used to treat the compressed poplar (Populus tomentosa) wood for permanent setting at 180 ℃ for 2 hours at various pressures of 0.1 MPa, 0.3 MPa, and 0.5 MPa. The variables that represented wood color, mass loss, and equilibrium moisture content (EMC) were measured. The results showed that the medium composition and pressure had significant impact on wood color changes. When L* decreased and a* increased consistently with the increasing pressures, wood surface color turned to red brown. When air only was used as the medium, △L* increased significantly with the increasing pressure. When steam only was used as the medium, a pressure of 0.5 MPa had a significant impact on △L*. When N2 only was used as the medium, the increasing pressure had no significant effect on △L*. The results of factorial analysis indicated that a certain relationship existed among the △L*, △E*, and △H*, between the △b* and △C*, and between the mass loss rate and EMC. Based on color changes, the clustering analysis results showed that the largest absolute values of △L* and △E* were 22.71 and 23.09 at 0.5 MPa respectively. Either 1/3 or 1/2 of air or N2 was added into the steam medium, △L* and △E* decreased more than 50%. Moreover, if the data was classified into 3 clusters, the similarity was shared among the clusters. If it was classified into 4 clusters, it could be further divided into 2 clusters: one was the treatment with air only and the mixed medium of steam and air, the other one was the treatment with a mixed medium of steam and N2. Through regulating the pressures and the mixing ratios of steam to air or N2, the color of the pressured wood can be controlled.关键词:Chinese white poplar wood (Populus tomentosa);surface-compressed wood;pressurized heat treatment;heating medium;wood color14|0|0更新时间:2025-09-11
摘要:Effects of heating media composition and its pressure on color changes in wood during permanent compression deformation were analyzed using statistical methods. The heating media, including steam only, air only, nitrogen (N2) only, and the mixture of either steam combining with air or steam combining with N2 were used to treat the compressed poplar (Populus tomentosa) wood for permanent setting at 180 ℃ for 2 hours at various pressures of 0.1 MPa, 0.3 MPa, and 0.5 MPa. The variables that represented wood color, mass loss, and equilibrium moisture content (EMC) were measured. The results showed that the medium composition and pressure had significant impact on wood color changes. When L* decreased and a* increased consistently with the increasing pressures, wood surface color turned to red brown. When air only was used as the medium, △L* increased significantly with the increasing pressure. When steam only was used as the medium, a pressure of 0.5 MPa had a significant impact on △L*. When N2 only was used as the medium, the increasing pressure had no significant effect on △L*. The results of factorial analysis indicated that a certain relationship existed among the △L*, △E*, and △H*, between the △b* and △C*, and between the mass loss rate and EMC. Based on color changes, the clustering analysis results showed that the largest absolute values of △L* and △E* were 22.71 and 23.09 at 0.5 MPa respectively. Either 1/3 or 1/2 of air or N2 was added into the steam medium, △L* and △E* decreased more than 50%. Moreover, if the data was classified into 3 clusters, the similarity was shared among the clusters. If it was classified into 4 clusters, it could be further divided into 2 clusters: one was the treatment with air only and the mixed medium of steam and air, the other one was the treatment with a mixed medium of steam and N2. Through regulating the pressures and the mixing ratios of steam to air or N2, the color of the pressured wood can be controlled.关键词:Chinese white poplar wood (Populus tomentosa);surface-compressed wood;pressurized heat treatment;heating medium;wood color14|0|0更新时间:2025-09-11 -
 摘要:In this study, a combination of surface compression and superheated steam treatment was conducted to improve the properties of poplar (Populus tomentosa) sapwood. The effects of surface compression and varying steam pressures (180 ℃, 0.1~0.7 MPa) on the cellular morphology and chemical structure of the surface-compressed wood were investigated using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). When the test temperature increased from 30 ℃ to 300 ℃, the reduction in the relative storage modules of the permanent setting wood treated with superheated steam (referred to as the permanent setting wood) was significantly greater than that of the control wood and the compressed wood. Compared to compressed wood, at a lower steam pressure (≤0.3 MPa), the loss modulus of the permanent setting wood showed no significant changes. However, when the steam pressure exceeded 0.5 MPa, both the peak temperature and apparent activation energy of α mechanical relaxation loss gradually decreased along with the increasing of steam pressures, by 11~45 ℃ and 22.89%~50.28%, respectively. After superheated steam treatment, deacetylation of hemicelluloses and lignin degradation reactions occurred in the compressed wood. This led to an increasing proportion of low molecular weight polymers and reducing the elasticity and viscosity recovery of the compressed wood. As a result, the dimensional stability was enhanced. The findings of this study provide a theoretical basis for the processing and utilization of surface-compressed wood with superheated steam treatment.关键词:wood;surface compression;superheated steam pressure;cell wall structure;chemical structure;dynamic viscoelastic properties42|0|0更新时间:2025-09-11
摘要:In this study, a combination of surface compression and superheated steam treatment was conducted to improve the properties of poplar (Populus tomentosa) sapwood. The effects of surface compression and varying steam pressures (180 ℃, 0.1~0.7 MPa) on the cellular morphology and chemical structure of the surface-compressed wood were investigated using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). When the test temperature increased from 30 ℃ to 300 ℃, the reduction in the relative storage modules of the permanent setting wood treated with superheated steam (referred to as the permanent setting wood) was significantly greater than that of the control wood and the compressed wood. Compared to compressed wood, at a lower steam pressure (≤0.3 MPa), the loss modulus of the permanent setting wood showed no significant changes. However, when the steam pressure exceeded 0.5 MPa, both the peak temperature and apparent activation energy of α mechanical relaxation loss gradually decreased along with the increasing of steam pressures, by 11~45 ℃ and 22.89%~50.28%, respectively. After superheated steam treatment, deacetylation of hemicelluloses and lignin degradation reactions occurred in the compressed wood. This led to an increasing proportion of low molecular weight polymers and reducing the elasticity and viscosity recovery of the compressed wood. As a result, the dimensional stability was enhanced. The findings of this study provide a theoretical basis for the processing and utilization of surface-compressed wood with superheated steam treatment.关键词:wood;surface compression;superheated steam pressure;cell wall structure;chemical structure;dynamic viscoelastic properties42|0|0更新时间:2025-09-11 -
 摘要:With a target compression ratio of 40%~65%, the compression deformation in the heartwood of Chinese fir was stabilized through heat treatment using a steam-air mixed medium with pressure. The effect of the compression ratio on wood density distribution, set recovery, and mechanical properties were studied. The results showed that both early wood and late wood were compressed at compression ratio of 40%. As the compression ratio increased, the wood's density also increased, while the internal density distribution became more consistent. With the heat treatment of steam-air at medium pressure, the hygroscopic/water absorption set recovery of Chinese fir at different compression ratios were reduced to 0%~0.63%. Under conditions including air-dried, high-humidity, and water absorption, there was almost no recovery occurred. With the increased compression ratio and density, the wood's hardness, bending strength (MOR, MOE), and compression strength perpendicular to grain continuously increased. There was a highly significant quadratic functional relationship between wood density and hardness. Meanwhile, there were extremely significant linear relationship between wood density and MOR, MOE, as well as compression strength perpendicular to grain, with the correlation coefficient being greater than 0.938. During radial loading under compression perpendicular to grain, typical stress-strain characteristics were not observed. At a compression ratio of 40%, the compressive strength perpendicular to grain under tangential loading increased by approximately 50%, however there was almost no increase under radial loading. When the compression ratio reached at least 45%, the compressive strength perpendicular to grain under both tangential and radial loading were almost the same. At a compression ratio of 65%, the compressive strength perpendicular to grain under both tangential and radial loading reached four times more than those of the control wood.关键词:Chinese fir heartwood;Compression ratio;set recovery;density;compressive strength perpendicular to grain26|0|0更新时间:2025-09-11
摘要:With a target compression ratio of 40%~65%, the compression deformation in the heartwood of Chinese fir was stabilized through heat treatment using a steam-air mixed medium with pressure. The effect of the compression ratio on wood density distribution, set recovery, and mechanical properties were studied. The results showed that both early wood and late wood were compressed at compression ratio of 40%. As the compression ratio increased, the wood's density also increased, while the internal density distribution became more consistent. With the heat treatment of steam-air at medium pressure, the hygroscopic/water absorption set recovery of Chinese fir at different compression ratios were reduced to 0%~0.63%. Under conditions including air-dried, high-humidity, and water absorption, there was almost no recovery occurred. With the increased compression ratio and density, the wood's hardness, bending strength (MOR, MOE), and compression strength perpendicular to grain continuously increased. There was a highly significant quadratic functional relationship between wood density and hardness. Meanwhile, there were extremely significant linear relationship between wood density and MOR, MOE, as well as compression strength perpendicular to grain, with the correlation coefficient being greater than 0.938. During radial loading under compression perpendicular to grain, typical stress-strain characteristics were not observed. At a compression ratio of 40%, the compressive strength perpendicular to grain under tangential loading increased by approximately 50%, however there was almost no increase under radial loading. When the compression ratio reached at least 45%, the compressive strength perpendicular to grain under both tangential and radial loading were almost the same. At a compression ratio of 65%, the compressive strength perpendicular to grain under both tangential and radial loading reached four times more than those of the control wood.关键词:Chinese fir heartwood;Compression ratio;set recovery;density;compressive strength perpendicular to grain26|0|0更新时间:2025-09-11
SPECIAL SUBJECT ON PERMANENT SETTING OF COMPRESSION WOOD
-
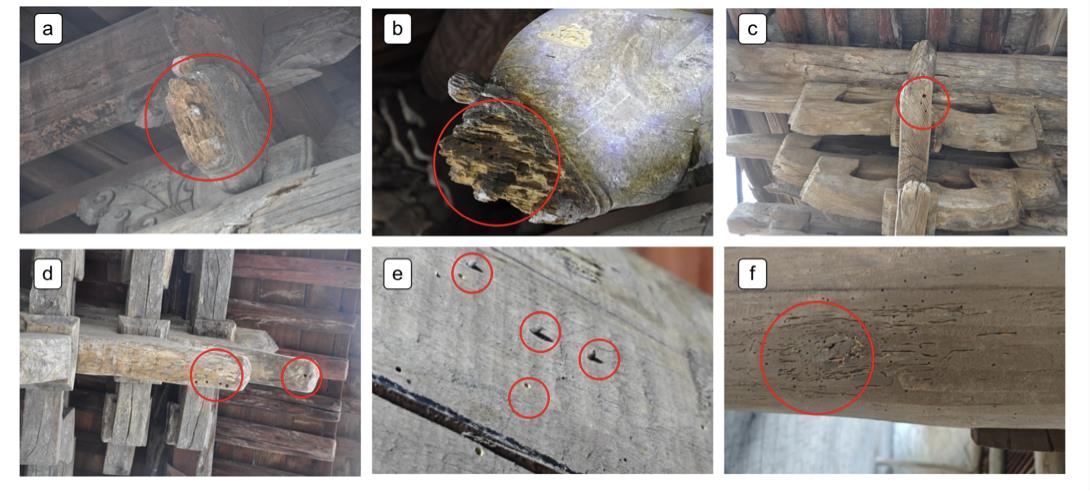 摘要:The southeast region of Shanxi Province is a treasure trove of ancient wooden buildings in China. Its ancient buildings have historical and cultural value. The numbers of ancient wooden buildings built in only Song and Jin dynasties in Shanxi account for more than 75% of amount in the whole country. Insect damage is one of the main threats to ancient wood buildings. The previous literature shows that there is a certain relationship between the insect-damaged wood of ancient buildings and trees planted in temple gardens. This article synthesizes relevant literature on wood-boring pests affecting ancient structures both within the southeast region of Shanxi Province and across China, combined with field surveys documenting pest damage and garden tree arrangements at specific sites in Jindongnan. It systematically analyzes the architectural characteristics of temples, prevailing patterns of garden tree configuration, and major insect types. Four categories of insects in ancient wood structures were identified as longhorn beetles (Cerambycidae), carpenter bees (Xylocopinae), Coleoptera wood-boring beetles include Lyctidae, Bostrychidae, and Anobiidae, and termites (Termitidae). Wood-boring beetle is the most prevalent (100%) and carpenter bees is the second most common (92%). On the basis of summarizing and sorting out the insect damage on wood structures and hosted trees, the principles of temple garden tree configuration are proposed for the prevention and control of insects in ancient buildings. It is called "tripartite principle", which integrates insect resistance, cultural significance, and ecological compatibility. This principle emphasizes avoiding high-risk tree species prone to inducing infestations, e.g., specific susceptible broad-leaved trees and flowering plants attractive to carpenter bees. Prioritizing species that embody religious and cultural symbolism while also offering potential pest-resistant or insect-repellent properties. Holistically considering ecological functions, the protection of ancient trees, and spatial layout factors. Continuously optimizing temple garden tree configuration schemes through practical application can significantly contribute to enhancing the integrated insect management system for protecting ancient architectural heritage.关键词:ancient timber architecture;insect infestation;tree configuration;temple gardens;southeast in Shanxi Province14|0|0更新时间:2025-09-11
摘要:The southeast region of Shanxi Province is a treasure trove of ancient wooden buildings in China. Its ancient buildings have historical and cultural value. The numbers of ancient wooden buildings built in only Song and Jin dynasties in Shanxi account for more than 75% of amount in the whole country. Insect damage is one of the main threats to ancient wood buildings. The previous literature shows that there is a certain relationship between the insect-damaged wood of ancient buildings and trees planted in temple gardens. This article synthesizes relevant literature on wood-boring pests affecting ancient structures both within the southeast region of Shanxi Province and across China, combined with field surveys documenting pest damage and garden tree arrangements at specific sites in Jindongnan. It systematically analyzes the architectural characteristics of temples, prevailing patterns of garden tree configuration, and major insect types. Four categories of insects in ancient wood structures were identified as longhorn beetles (Cerambycidae), carpenter bees (Xylocopinae), Coleoptera wood-boring beetles include Lyctidae, Bostrychidae, and Anobiidae, and termites (Termitidae). Wood-boring beetle is the most prevalent (100%) and carpenter bees is the second most common (92%). On the basis of summarizing and sorting out the insect damage on wood structures and hosted trees, the principles of temple garden tree configuration are proposed for the prevention and control of insects in ancient buildings. It is called "tripartite principle", which integrates insect resistance, cultural significance, and ecological compatibility. This principle emphasizes avoiding high-risk tree species prone to inducing infestations, e.g., specific susceptible broad-leaved trees and flowering plants attractive to carpenter bees. Prioritizing species that embody religious and cultural symbolism while also offering potential pest-resistant or insect-repellent properties. Holistically considering ecological functions, the protection of ancient trees, and spatial layout factors. Continuously optimizing temple garden tree configuration schemes through practical application can significantly contribute to enhancing the integrated insect management system for protecting ancient architectural heritage.关键词:ancient timber architecture;insect infestation;tree configuration;temple gardens;southeast in Shanxi Province14|0|0更新时间:2025-09-11
KEY SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH BASE OF HISTORICAL BUILDING WOOD
-
 摘要:In order to study the mechanical properties of ancient timber architecture damaged mortise-tenon joints, loosen damage type was selection, and the degradation laws of the penetrated mortise-tenon joints was studied. Four transparent mortise-tenon joints with different loosen rates were designed, and the bending moment-angle hysteresis curves were obtained by applying low cyclic loads. Hysteresis characteristics, skeleton curves, strength degradation, bearing capacity and deformation performance were analyzed. The experimental results indicate that the bending failure occurs in all the joints. The hysteresis curve of the specimen is “Z” shape, and the pinching effect is significant. With the increase of control displacement, the strength of the specimen decreases significantly. With the increase of the loosen rate, the area surrounded by the hysteresis curve of the joint decreases, the energy dissipation capacity weakens, the ultimate bending moment decreases gradually, and the angle increases gradually. Based on experimental investigations, numerical simulation analysis of the mortise-tenon joints was conducted using ABAQUS software to examine the effects of loosen degree on their mechanical performance. The results demonstrate that with the progression of loosen degree, both the load-bearing capacity and lateral stiffness exhibit degradation. According to experimental research results, it is recommended to define a loosening degree of 5%~10% as the critical threshold range for reinforcement decision-making.关键词:ancient timber architecture;through-tenon;performance degradation;FEM;parametric analysis40|0|0更新时间:2025-09-11
摘要:In order to study the mechanical properties of ancient timber architecture damaged mortise-tenon joints, loosen damage type was selection, and the degradation laws of the penetrated mortise-tenon joints was studied. Four transparent mortise-tenon joints with different loosen rates were designed, and the bending moment-angle hysteresis curves were obtained by applying low cyclic loads. Hysteresis characteristics, skeleton curves, strength degradation, bearing capacity and deformation performance were analyzed. The experimental results indicate that the bending failure occurs in all the joints. The hysteresis curve of the specimen is “Z” shape, and the pinching effect is significant. With the increase of control displacement, the strength of the specimen decreases significantly. With the increase of the loosen rate, the area surrounded by the hysteresis curve of the joint decreases, the energy dissipation capacity weakens, the ultimate bending moment decreases gradually, and the angle increases gradually. Based on experimental investigations, numerical simulation analysis of the mortise-tenon joints was conducted using ABAQUS software to examine the effects of loosen degree on their mechanical performance. The results demonstrate that with the progression of loosen degree, both the load-bearing capacity and lateral stiffness exhibit degradation. According to experimental research results, it is recommended to define a loosening degree of 5%~10% as the critical threshold range for reinforcement decision-making.关键词:ancient timber architecture;through-tenon;performance degradation;FEM;parametric analysis40|0|0更新时间:2025-09-11 -
 摘要:Bamboo strip composites were fabricated using vacuum infusion process (VIP), with two-dimensional woven fabrics prepared by stitching technique as reinforcements. The effects of stitch spacing and layup configuration (symmetrical and staggered forming) on mechanical properties were investigated. Results showed that at 8 cm stitch spacing, unidirectional composites in the 0° direction exhibited increased tensile, flexural, and impact strengths by 7.6%, 5.6%, and 15.3%, respectively, compared to non-stitched samples. Furthermore, the staggered distribution of stitching threads across layers effectively mitigated stress concentration. However, excessively small stitch spacing causes damages in bamboo strips and resin-rich zones, reducing mechanical properties in the 0° direction. Furthermore, layup configuration significantly influences mechanical performance. Tensile properties improve with increasing concentration of unidirectional fiber layers, and the [90/0/0]s configuration exhibits optimal performance in 0° direction, with tensile strength and modulus reaching 183 MPa and 20.4 GPa, respectively. Flexural properties are governed by surface layer orientation, with the [0/0/90]s configuration showing maximum flexural strength (320.4 MPa) and modulus (17.1 GPa) in 0° direction, along with superior deformation resistance. The [90/0/0]s configuration demonstrates optimal impact strength (91.4 kJ/m²) in 0° direction, attributed to the continuous distribution of 0° bamboo strip that effectively mitigates stress concentration. Various layup configuration effectively affect the mechanical properties of bamboo strip composites. This study provides design basis for the engineering application of bamboo-strip composites through the optimization of both process and structure.关键词:bamboo strips composites;vacuum infusion process;mechanical properties;stitch row spacing;lay-up configuration13|0|0更新时间:2025-09-11
摘要:Bamboo strip composites were fabricated using vacuum infusion process (VIP), with two-dimensional woven fabrics prepared by stitching technique as reinforcements. The effects of stitch spacing and layup configuration (symmetrical and staggered forming) on mechanical properties were investigated. Results showed that at 8 cm stitch spacing, unidirectional composites in the 0° direction exhibited increased tensile, flexural, and impact strengths by 7.6%, 5.6%, and 15.3%, respectively, compared to non-stitched samples. Furthermore, the staggered distribution of stitching threads across layers effectively mitigated stress concentration. However, excessively small stitch spacing causes damages in bamboo strips and resin-rich zones, reducing mechanical properties in the 0° direction. Furthermore, layup configuration significantly influences mechanical performance. Tensile properties improve with increasing concentration of unidirectional fiber layers, and the [90/0/0]s configuration exhibits optimal performance in 0° direction, with tensile strength and modulus reaching 183 MPa and 20.4 GPa, respectively. Flexural properties are governed by surface layer orientation, with the [0/0/90]s configuration showing maximum flexural strength (320.4 MPa) and modulus (17.1 GPa) in 0° direction, along with superior deformation resistance. The [90/0/0]s configuration demonstrates optimal impact strength (91.4 kJ/m²) in 0° direction, attributed to the continuous distribution of 0° bamboo strip that effectively mitigates stress concentration. Various layup configuration effectively affect the mechanical properties of bamboo strip composites. This study provides design basis for the engineering application of bamboo-strip composites through the optimization of both process and structure.关键词:bamboo strips composites;vacuum infusion process;mechanical properties;stitch row spacing;lay-up configuration13|0|0更新时间:2025-09-11 -
 摘要:Surface decorated blockboard with impregnated paper has become a dominant material for custom furniture because of its attractive appearance, environmental friendliness, and durability. Nevertheless, during the process of production and in the middle of service, the board frequently develops cracks on the surface that impair both its aesthetics and performance. To address this issue, the effects of reconstituted decorative veneer and melamine-impregnated film paper were investigated on the crack resistance performance of film overlaid blockboard. The study revealed that impregnated film paper with a basis weight below 80 g/m² exhibited significantly better tensile properties than paper heavier than 80 g/m². Wood-grain paper outperforms solid-color paper in tensile behavior; compared with solid-color paper of the same basis weight, wood-grain paper showed increased elongation at break and higher tensile strength. Because the tensile properties of impregnated film paper directly determine the crack resistance of the decorated blockboard, these differences were critical. In addition, increasing the moisture content of the reconstituted decorative veneer to 21% prevented cracking in the decorated blockboard within the 24 hours specified in the crack resistance test under the temperature-humidity conditions defined by GB/T 17657—2022 “Test methods of evaluating the properties of wood-based panels and surface decorated wood-based panels”; however, this protection was not consistent beyond 24 hours. Aqueous silicone resin modification established a dual protective mechanism: it significantly reduced the shrinkage of the reconstituted decorative veneer and simultaneously improved its transverse tensile properties, thereby enhanced the crack resistance of impregnated film paper-decorated blockboard. The modified system stayed stable up to 72 hours.关键词:film overlaid blockboard;reconstituted decorative veneer;impregnated paper;silicone resin;crack resistance53|0|0更新时间:2025-09-11
摘要:Surface decorated blockboard with impregnated paper has become a dominant material for custom furniture because of its attractive appearance, environmental friendliness, and durability. Nevertheless, during the process of production and in the middle of service, the board frequently develops cracks on the surface that impair both its aesthetics and performance. To address this issue, the effects of reconstituted decorative veneer and melamine-impregnated film paper were investigated on the crack resistance performance of film overlaid blockboard. The study revealed that impregnated film paper with a basis weight below 80 g/m² exhibited significantly better tensile properties than paper heavier than 80 g/m². Wood-grain paper outperforms solid-color paper in tensile behavior; compared with solid-color paper of the same basis weight, wood-grain paper showed increased elongation at break and higher tensile strength. Because the tensile properties of impregnated film paper directly determine the crack resistance of the decorated blockboard, these differences were critical. In addition, increasing the moisture content of the reconstituted decorative veneer to 21% prevented cracking in the decorated blockboard within the 24 hours specified in the crack resistance test under the temperature-humidity conditions defined by GB/T 17657—2022 “Test methods of evaluating the properties of wood-based panels and surface decorated wood-based panels”; however, this protection was not consistent beyond 24 hours. Aqueous silicone resin modification established a dual protective mechanism: it significantly reduced the shrinkage of the reconstituted decorative veneer and simultaneously improved its transverse tensile properties, thereby enhanced the crack resistance of impregnated film paper-decorated blockboard. The modified system stayed stable up to 72 hours.关键词:film overlaid blockboard;reconstituted decorative veneer;impregnated paper;silicone resin;crack resistance53|0|0更新时间:2025-09-11 -
 摘要:Aiming at the problems of large number of deep learning model parameters and low classification and detection accuracy in the field of wood defect detection, a lightweight detection model YOLOv8N-HCDP based on YOLOv8n was proposed. Firstly, the lightweight backbone network of HgNetv2 (high performance GPU network v2) is constructed. Secondly, a new CCFM-dy module is obtained by Dynamic Head fusion with lightweight cross-scale feature fusion module (CCFM) to replace the traditional neck network and detection head, reducing the number of model parameters and calculation amount. Dynamic convolution is introduced to make the network benefit from large-scale training while maintaining low computation. Finally, an innovative PPC structure is introduced to replace CSP bottleneck(C2f)in the network structure to further lightweight the model. The experimental results show that compared with the benchmark model, the improved model has 54.15% less parameters, 44.44% less computation, 51.42% less volume, and 2.0% more mAP50, which is more suitable for deployment on embedded devices with limited hardware resources. It provides a more efficient defect detection solution for the wood processing industry.关键词:wood defect detection;YOLOv8n;light weight;HgNetv2;mAP16|0|0更新时间:2025-09-11
摘要:Aiming at the problems of large number of deep learning model parameters and low classification and detection accuracy in the field of wood defect detection, a lightweight detection model YOLOv8N-HCDP based on YOLOv8n was proposed. Firstly, the lightweight backbone network of HgNetv2 (high performance GPU network v2) is constructed. Secondly, a new CCFM-dy module is obtained by Dynamic Head fusion with lightweight cross-scale feature fusion module (CCFM) to replace the traditional neck network and detection head, reducing the number of model parameters and calculation amount. Dynamic convolution is introduced to make the network benefit from large-scale training while maintaining low computation. Finally, an innovative PPC structure is introduced to replace CSP bottleneck(C2f)in the network structure to further lightweight the model. The experimental results show that compared with the benchmark model, the improved model has 54.15% less parameters, 44.44% less computation, 51.42% less volume, and 2.0% more mAP50, which is more suitable for deployment on embedded devices with limited hardware resources. It provides a more efficient defect detection solution for the wood processing industry.关键词:wood defect detection;YOLOv8n;light weight;HgNetv2;mAP16|0|0更新时间:2025-09-11
RESEARCH PAPERS
-
 摘要:In order to achieve automated and efficient sorting of sawn timber with various surface conditions, a sawn timber automatic sorting system integrated with machine vision is designed. The entire system is mainly composed of modules including sawn timber conveyance, sawn timber automatic flipping, sawn timber inspection, and automatic sorting. The mechanical structure comprises chain conveying and a multi-stage automatic sorting, while the control system features sawn timber machine vision inspection and overall motion control functions. The control system adopts high-performance image acquisition and processing of sawn timber to identify surface defects such as live knots, dead knots, and wormholes. Based on the image analysis results, it controls the sorting motion system to achieve real-time grading and sorting of sawn timber. The prototype conducted real-time detection and sorting of defects such as living knot, dead knot, and insect hole on both sides of sawn timber. The recognition rates were 86.67%, 86.67%, and 80.00% respectively, which verified the feasibility of the sorting system operation.关键词:sawn timber;sorting;machine vision;defect detection;real-time control15|0|0更新时间:2025-09-11
摘要:In order to achieve automated and efficient sorting of sawn timber with various surface conditions, a sawn timber automatic sorting system integrated with machine vision is designed. The entire system is mainly composed of modules including sawn timber conveyance, sawn timber automatic flipping, sawn timber inspection, and automatic sorting. The mechanical structure comprises chain conveying and a multi-stage automatic sorting, while the control system features sawn timber machine vision inspection and overall motion control functions. The control system adopts high-performance image acquisition and processing of sawn timber to identify surface defects such as live knots, dead knots, and wormholes. Based on the image analysis results, it controls the sorting motion system to achieve real-time grading and sorting of sawn timber. The prototype conducted real-time detection and sorting of defects such as living knot, dead knot, and insect hole on both sides of sawn timber. The recognition rates were 86.67%, 86.67%, and 80.00% respectively, which verified the feasibility of the sorting system operation.关键词:sawn timber;sorting;machine vision;defect detection;real-time control15|0|0更新时间:2025-09-11
RESEARCH BRIEFING
0

