
最新刊期
卷 39 , 期 5 , 2025
-
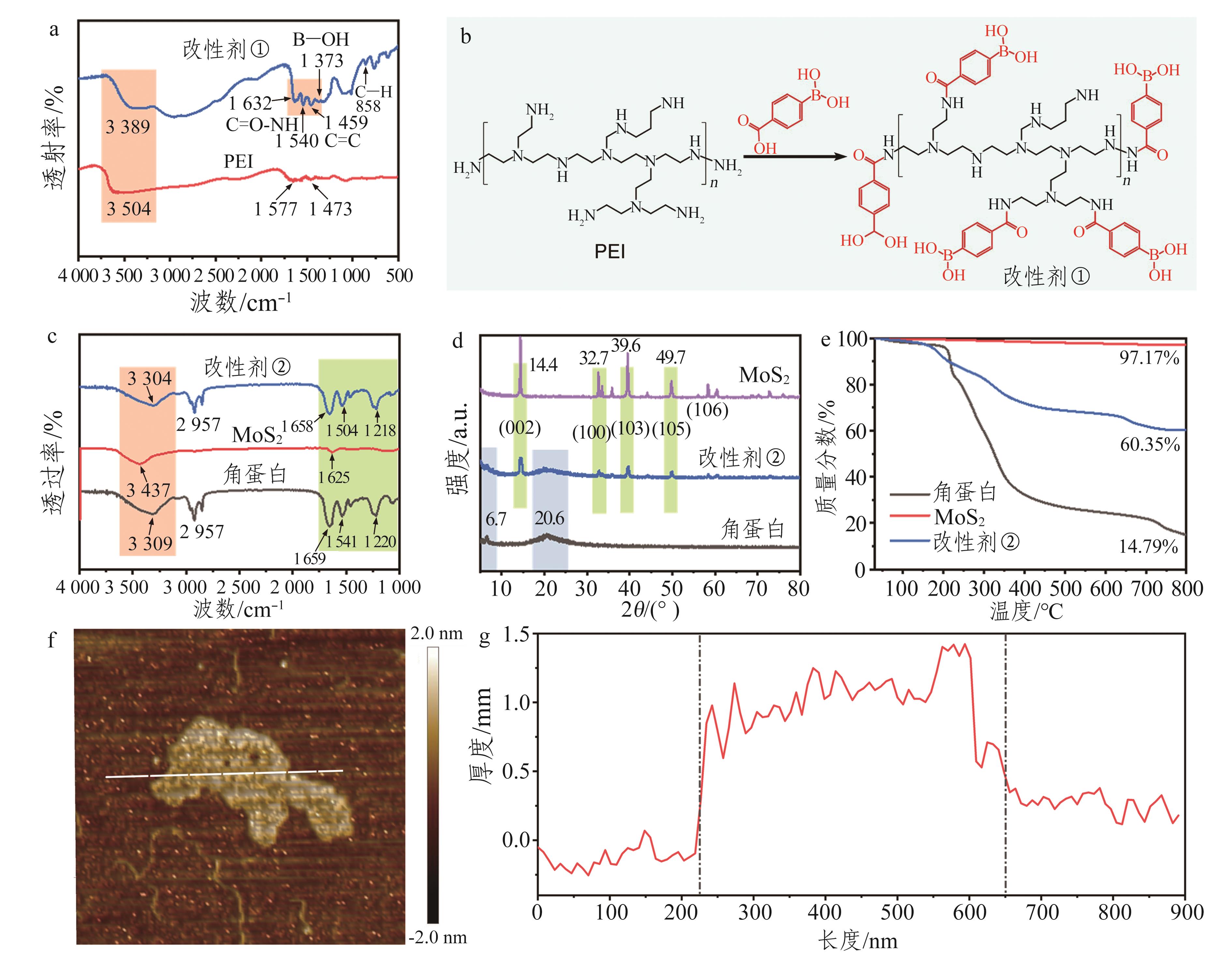 摘要:The application of soy-based adhesives is limited due to its poor water resistance, susceptibility to mildew, and incompatibility with particleboard manufacturing processes. To overcome these shortcomings, this study improved the adhesive’s performance by synergetic modification using MoS2 and polyethyleneimine, and tested the physical-mechanical properties and mildew resistance of particleboard. Results showed that the modified soy-based adhesive exhibited a dense fracture structure, improved cohesive strength and water resistance, and excellent mildew resistance. The fabricated three-layer particleboard demonstrated excellent physical and mechanical properties, including a static flexural strength of 19.20 MPa, elastic modulus of 2.77 GPa, internal bonding strength of 0.73 MPa, surface bonding strength of 1.10 MPa, and a 2-h water absorption thickness expansion rate of 1.88%, which met the Type P2 requirements specified in GB/T 4897—2015 Particleboard. Notably, the particleboard achieved a mildew resistance with an infection grading value exceeding level 1 according to LY/T 2230—2013 Standard method of evaluating the resistance of wood-based panels to mold. These properties demonstrated a great potential of using the modified soy-based adhesive in manufacturing particleboards.关键词:soy-based adhesive;particleboard;organic-inorganic hybrid modification;water resistance;mildew resistance;mechanical properties2|0|0更新时间:2025-12-15
摘要:The application of soy-based adhesives is limited due to its poor water resistance, susceptibility to mildew, and incompatibility with particleboard manufacturing processes. To overcome these shortcomings, this study improved the adhesive’s performance by synergetic modification using MoS2 and polyethyleneimine, and tested the physical-mechanical properties and mildew resistance of particleboard. Results showed that the modified soy-based adhesive exhibited a dense fracture structure, improved cohesive strength and water resistance, and excellent mildew resistance. The fabricated three-layer particleboard demonstrated excellent physical and mechanical properties, including a static flexural strength of 19.20 MPa, elastic modulus of 2.77 GPa, internal bonding strength of 0.73 MPa, surface bonding strength of 1.10 MPa, and a 2-h water absorption thickness expansion rate of 1.88%, which met the Type P2 requirements specified in GB/T 4897—2015 Particleboard. Notably, the particleboard achieved a mildew resistance with an infection grading value exceeding level 1 according to LY/T 2230—2013 Standard method of evaluating the resistance of wood-based panels to mold. These properties demonstrated a great potential of using the modified soy-based adhesive in manufacturing particleboards.关键词:soy-based adhesive;particleboard;organic-inorganic hybrid modification;water resistance;mildew resistance;mechanical properties2|0|0更新时间:2025-12-15
GREEN MANUFACTURING OF WOOD-BASED MATERIALS
-
 摘要:The width and number of annual rings are a good reference for dating the timber components in ancient architecture, which is needed to balance the requirements of cultural relics and measurement accuracy. Larch (Larix gmelinii var. principis-rupprechtii) and poplar (Populus deltoides×Populus cathayana) were commonly used for constructing buildings in ancient China. The wood samples were obtained at heights of 1 200~1 400 mm and 2 400~2 600 mm from these trees. The drill resistance (DR) and computed tomography (CT) methods were used and compared with the traditional photography method applied on transverse surface of wood. The results showed that CT was superior to DR in detection of both annual ring width and number. The accuracy of DR in tree-ring width detection differed from that of CT by less than 3%. The large error appeared in detection of annual ring number using DR, which was mainly due to the difficulty of its detection path accurately passing through the pith. When CT and DR were employed to measure annual rings, tree species with stable growth and clear annual rings should be prioritized, and the measurements should be carried out at the trunk without obvious defects. The detection height should be determined based on the growth characteristics of the wood.关键词:annual ring width;annual ring number;drill resistance;computed tomography2|0|0更新时间:2025-12-15
摘要:The width and number of annual rings are a good reference for dating the timber components in ancient architecture, which is needed to balance the requirements of cultural relics and measurement accuracy. Larch (Larix gmelinii var. principis-rupprechtii) and poplar (Populus deltoides×Populus cathayana) were commonly used for constructing buildings in ancient China. The wood samples were obtained at heights of 1 200~1 400 mm and 2 400~2 600 mm from these trees. The drill resistance (DR) and computed tomography (CT) methods were used and compared with the traditional photography method applied on transverse surface of wood. The results showed that CT was superior to DR in detection of both annual ring width and number. The accuracy of DR in tree-ring width detection differed from that of CT by less than 3%. The large error appeared in detection of annual ring number using DR, which was mainly due to the difficulty of its detection path accurately passing through the pith. When CT and DR were employed to measure annual rings, tree species with stable growth and clear annual rings should be prioritized, and the measurements should be carried out at the trunk without obvious defects. The detection height should be determined based on the growth characteristics of the wood.关键词:annual ring width;annual ring number;drill resistance;computed tomography2|0|0更新时间:2025-12-15
KEY SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH BASE OF HISTORICAL BUILDING WOOD
-
 摘要:Carbon dots have attracted significant attention due to their unique quantum size effect, excellent optical absorption and conversion properties, good dispersibility, and eco-friendly and non-toxic characteristics. The synthesis of carbon dots is generally categorized into top-down approaches (e.g., laser ablation) and bottom-up methods (e.g., microwave synthesis, pyrolysis, and hydrothermal treatment). Among these methods, hydrothermal treatment stands out for its adaptability to broad raw material sources, simple preparation process, excellent water dispersibility, and facile surface functionalization, making it one of the mainstream methods for preparing fluorescent carbon nanomaterials. This review summarizes the main preparation methods, basic properties, and formation mechanisms of fluorescent carbon dots, as well as their applications in the fields of wood-based functional materials such as photocatalysis, photoaging resistance, flame retardancy, antibacterial performance and adhesives. The prospects for the development of carbon dots in novel wood-based functional materials are also proposed.关键词:wood-based functional materials;carbon dots;preparation methods;hydrothermal treatment;functionalization2|0|0更新时间:2025-12-15
摘要:Carbon dots have attracted significant attention due to their unique quantum size effect, excellent optical absorption and conversion properties, good dispersibility, and eco-friendly and non-toxic characteristics. The synthesis of carbon dots is generally categorized into top-down approaches (e.g., laser ablation) and bottom-up methods (e.g., microwave synthesis, pyrolysis, and hydrothermal treatment). Among these methods, hydrothermal treatment stands out for its adaptability to broad raw material sources, simple preparation process, excellent water dispersibility, and facile surface functionalization, making it one of the mainstream methods for preparing fluorescent carbon nanomaterials. This review summarizes the main preparation methods, basic properties, and formation mechanisms of fluorescent carbon dots, as well as their applications in the fields of wood-based functional materials such as photocatalysis, photoaging resistance, flame retardancy, antibacterial performance and adhesives. The prospects for the development of carbon dots in novel wood-based functional materials are also proposed.关键词:wood-based functional materials;carbon dots;preparation methods;hydrothermal treatment;functionalization2|0|0更新时间:2025-12-15
REVIEWS
-
 摘要:To address the limitations of existing theoretical models for predicting the minimum ignition energy (MIE) of wood dust, such as the lack of coupling between combustion dynamics and heat transfer and the insufficient prediction accuracy, this study proposes a “Spherical Layer Energy Iteration Model”. In the model, the ignition space is divided into multiple spherical layers, assuming that the dust in each layer burns continuously within a short period to form an explosion propagation process. By introducing the Arrhenius equation to calculate the combustion reaction duration and incorporating interlayer heat conduction energy balance, the model iteratively computes the supplementary energy required from the ignition source layer by layer, ultimately obtaining the MIE. The model was applied to calculate the MIE of medium density fiberboard wood dust with particle size between 0~500 μm and mass concentration from 0.25~2.0 g/L. When compared with experimental data obtained in accordance with the BS EN 13821-2002 standard (Ref. [7]), the proposed model exhibited an average deviation of only 4% and a maximum deviation of 7%, whereas traditional mechanistic models showed deviations of about 60% (Ref. [15]). This outcome validates the model’s significant improvement in accuracy and applicability.关键词:wood dust;minimum ignition energy;mass concentration;particle size;theoretical simulation2|0|0更新时间:2025-12-15
摘要:To address the limitations of existing theoretical models for predicting the minimum ignition energy (MIE) of wood dust, such as the lack of coupling between combustion dynamics and heat transfer and the insufficient prediction accuracy, this study proposes a “Spherical Layer Energy Iteration Model”. In the model, the ignition space is divided into multiple spherical layers, assuming that the dust in each layer burns continuously within a short period to form an explosion propagation process. By introducing the Arrhenius equation to calculate the combustion reaction duration and incorporating interlayer heat conduction energy balance, the model iteratively computes the supplementary energy required from the ignition source layer by layer, ultimately obtaining the MIE. The model was applied to calculate the MIE of medium density fiberboard wood dust with particle size between 0~500 μm and mass concentration from 0.25~2.0 g/L. When compared with experimental data obtained in accordance with the BS EN 13821-2002 standard (Ref. [7]), the proposed model exhibited an average deviation of only 4% and a maximum deviation of 7%, whereas traditional mechanistic models showed deviations of about 60% (Ref. [15]). This outcome validates the model’s significant improvement in accuracy and applicability.关键词:wood dust;minimum ignition energy;mass concentration;particle size;theoretical simulation2|0|0更新时间:2025-12-15 -
Detection of Simulated Blister in Medium Density Fiberboard Using Ultrasonic Phase Difference Method
 摘要:Blister, a common defect that frequently appears during the production of medium density fiberboard (MDF), compromises its performance. To accurately detecting these internal defects, this study proposes an ultrasonic phase-difference method specifically tailored for MDF. Six MDF panels of various thicknesses were fabricated. Artificial blisters were constructed in order to systematically investigate the ultrasonic phase characteristics in both defect-free and blister-simulation regions using an oscilloscope and a power amplifier. When ultrasonic waves traverse defect-free MDF, the phase exhibits a periodic variation between -180° and +180°. In contrast, when the wave interacts with a blister, the phase remains within the same range only if the excitation frequency is below 230 kHz, while when it is above 230 kHz, the phase range collapses abruptly to between -50° and +50°. Consequently, frequencies of 230 kHz and higher are recommended for reliable blister detection. A strong linear correlation (Pearson’s r≈0.9) was formed between the measured phase and the geometrical attributes of the blister: its depth from the surface and its thickness. Specifically, the phase increases monotonically with increasing both defect depth and thickness. The proposed method offers a non-destructive, depth-resolving inspection solution that can be integrated into industrial MDF production lines, thereby offering significant value for the realization of online, automated, and intelligent quality monitoring of fiberboard production.关键词:medium density fiberboard;nondestructive testing;Ultrasonic;blister;phase difference2|0|0更新时间:2025-12-15
摘要:Blister, a common defect that frequently appears during the production of medium density fiberboard (MDF), compromises its performance. To accurately detecting these internal defects, this study proposes an ultrasonic phase-difference method specifically tailored for MDF. Six MDF panels of various thicknesses were fabricated. Artificial blisters were constructed in order to systematically investigate the ultrasonic phase characteristics in both defect-free and blister-simulation regions using an oscilloscope and a power amplifier. When ultrasonic waves traverse defect-free MDF, the phase exhibits a periodic variation between -180° and +180°. In contrast, when the wave interacts with a blister, the phase remains within the same range only if the excitation frequency is below 230 kHz, while when it is above 230 kHz, the phase range collapses abruptly to between -50° and +50°. Consequently, frequencies of 230 kHz and higher are recommended for reliable blister detection. A strong linear correlation (Pearson’s r≈0.9) was formed between the measured phase and the geometrical attributes of the blister: its depth from the surface and its thickness. Specifically, the phase increases monotonically with increasing both defect depth and thickness. The proposed method offers a non-destructive, depth-resolving inspection solution that can be integrated into industrial MDF production lines, thereby offering significant value for the realization of online, automated, and intelligent quality monitoring of fiberboard production.关键词:medium density fiberboard;nondestructive testing;Ultrasonic;blister;phase difference2|0|0更新时间:2025-12-15 -
 摘要:Among various types of historical architecture, beam-lifting timber frames, especially those used in traditional wooden structures in China, are the key components. The beam-lifting timber frame structure is known for its spacious internal layout and large load-bearing capacity, which are critical factors for its large-span use. However, there is limited research on the creep behavior of these timber frames over long-term loading situation, especially at the critical joint areas where significant stress concentration occurs. Based on the prototype of a Chinese fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata) beam-lifting timber frame connected by straight tenon joints, a three-dimensional digital model was constructed using Solidworks software. The finite element analysis software ANSYS Workbench was employed to simulate and analyze the load capacity, allowable deformation limit, and the variation of strain over time during creep. Finally, the Findley's power law model was used to analyze the strain evolution law and performance degradation mechanism caused by the creep in the wooden frame under various load levels. The results showed that the straight tenon joint area was the most vulnerable part of the timber frame, as it yielded first when the load reached the load limit. Additionally, the steady-state creep stage showed that the creep strain was linearly related to time under various loads, highlighting the progressive deformation of the structure. Notably, under the same load, the strain growth rate at the node of the golden column was significantly greater than that of the five-beam structure, indicating that the column experiences more pronounced creep deformation due to the axial pressure it bore. This finding suggested that the column was more susceptible to long-term load-induced deformation than other parts of the structure. This research provided a reference for understanding the impact of long-term loading and creep on the mechanical properties of timber joints, specifically straight tenon joints, in ancient buildings. It also offered valuable insights into the load threshold setting and maintenance strategies for the conservation of timber frame historical wooden structures.关键词:beam-lifting timber frame;straight tenon joint;creep behavior;mechanical performance of joints;finite element analysis2|0|0更新时间:2025-12-15
摘要:Among various types of historical architecture, beam-lifting timber frames, especially those used in traditional wooden structures in China, are the key components. The beam-lifting timber frame structure is known for its spacious internal layout and large load-bearing capacity, which are critical factors for its large-span use. However, there is limited research on the creep behavior of these timber frames over long-term loading situation, especially at the critical joint areas where significant stress concentration occurs. Based on the prototype of a Chinese fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata) beam-lifting timber frame connected by straight tenon joints, a three-dimensional digital model was constructed using Solidworks software. The finite element analysis software ANSYS Workbench was employed to simulate and analyze the load capacity, allowable deformation limit, and the variation of strain over time during creep. Finally, the Findley's power law model was used to analyze the strain evolution law and performance degradation mechanism caused by the creep in the wooden frame under various load levels. The results showed that the straight tenon joint area was the most vulnerable part of the timber frame, as it yielded first when the load reached the load limit. Additionally, the steady-state creep stage showed that the creep strain was linearly related to time under various loads, highlighting the progressive deformation of the structure. Notably, under the same load, the strain growth rate at the node of the golden column was significantly greater than that of the five-beam structure, indicating that the column experiences more pronounced creep deformation due to the axial pressure it bore. This finding suggested that the column was more susceptible to long-term load-induced deformation than other parts of the structure. This research provided a reference for understanding the impact of long-term loading and creep on the mechanical properties of timber joints, specifically straight tenon joints, in ancient buildings. It also offered valuable insights into the load threshold setting and maintenance strategies for the conservation of timber frame historical wooden structures.关键词:beam-lifting timber frame;straight tenon joint;creep behavior;mechanical performance of joints;finite element analysis2|0|0更新时间:2025-12-15 -
 摘要:In recent years, the nesting behavior of carpenter bees in wooden structural components has emerged as a significant conservation challenge for ancient timber buildings. As vital pollinators, these insects cannot be indiscriminately eliminated with conventional insecticides. Instead, an eco-friendly mitigation strategy involves the use of behavioral repellents to alter their nesting behavior, thereby reducing their impact on historical wooden structures while preserving their ecological role. This study targeting on two species, Xylocopa appendiculata and Xylocopa rufipes, employs a dual-choice olfactometer to screen highly effective repellent and determine their optimal mass fraction. The permeability, loading capacity, and volatility of these repellents in Chinese fir were evaluated, and the repellent efficacy of the treated wood was comprehensively analyzed. The results demonstrated that α-phellandrene (9%), menthol volatile oil (80%), benzyl acetate (2%) and benzyl benzoate (10%) exhibited Grade IV repellency against Xylocopa appendiculata, while menthol volatile oil (80%) and benzyl benzoate (10%) exhibited Grade IV of repellency against Xylocopa rufipes. Wood treated with benzyl acetate (0.09 kg/m³) and benzyl benzoate (0.48 kg/m³) exhibited Grade IV of repellency against Xylocopa appendiculata, while limonene (0.28 kg/m³) and benzyl benzoate (0.71 kg/m³) treated wood exhibited Grade III against Xylocopa rufipes. These three formulations maintained persistent repellent effects for at least 10 days. This study explores eco-friendly control techniques for mitigating carpenter bees (Xylocopa spp.) to prevent damage to wooden components in historic buildings, offering novel theoretical and practical approaches to the conservation of ancient timber structures.关键词:carpenter bee damage;repellent;loading capacity;grade of repellency;applicability;Cunninghamia lanceolata2|0|0更新时间:2025-12-15
摘要:In recent years, the nesting behavior of carpenter bees in wooden structural components has emerged as a significant conservation challenge for ancient timber buildings. As vital pollinators, these insects cannot be indiscriminately eliminated with conventional insecticides. Instead, an eco-friendly mitigation strategy involves the use of behavioral repellents to alter their nesting behavior, thereby reducing their impact on historical wooden structures while preserving their ecological role. This study targeting on two species, Xylocopa appendiculata and Xylocopa rufipes, employs a dual-choice olfactometer to screen highly effective repellent and determine their optimal mass fraction. The permeability, loading capacity, and volatility of these repellents in Chinese fir were evaluated, and the repellent efficacy of the treated wood was comprehensively analyzed. The results demonstrated that α-phellandrene (9%), menthol volatile oil (80%), benzyl acetate (2%) and benzyl benzoate (10%) exhibited Grade IV repellency against Xylocopa appendiculata, while menthol volatile oil (80%) and benzyl benzoate (10%) exhibited Grade IV of repellency against Xylocopa rufipes. Wood treated with benzyl acetate (0.09 kg/m³) and benzyl benzoate (0.48 kg/m³) exhibited Grade IV of repellency against Xylocopa appendiculata, while limonene (0.28 kg/m³) and benzyl benzoate (0.71 kg/m³) treated wood exhibited Grade III against Xylocopa rufipes. These three formulations maintained persistent repellent effects for at least 10 days. This study explores eco-friendly control techniques for mitigating carpenter bees (Xylocopa spp.) to prevent damage to wooden components in historic buildings, offering novel theoretical and practical approaches to the conservation of ancient timber structures.关键词:carpenter bee damage;repellent;loading capacity;grade of repellency;applicability;Cunninghamia lanceolata2|0|0更新时间:2025-12-15
RESEARCH PAPERS
-
 摘要:By regulating temperature and humidity conditions, the curing process of magnesium oxychloride adhesive can be optimized; the microstructure and properties of inorganic plywood can be improved as well. Plywood from Cunninghamia lanceolata veneer with magnesium oxychloride adhesive was prepared under different temperature and humidity conditions during the curing environment. The curing time, microstructure, and plywood properties of magnesium oxychloride adhesive were experimentally tested. Microscopic analysis showed that suitable temperature and humidity promotes the oriented growth of 518 phase crystals (5 Mg(OH)₂•MgCl₂•8H₂O) and inhibits the formation of Mg(OH)₂, which significantly enhance the cross-linking density of the adhesive. Under conditions of 70 °C and 30% relative humidity, the content of 518 phase crystals in the adhesive reached its peak, forming a dense and orderly microstructure inside the plywood, resulting in an increase of static bending strength to 54 MPa and an increase of elastic modulus to 7 407 MPa, which was improved by 44.8% and 39.1% compared to the control samples cured under conventional conditions; the bond strength reaches 0.98 MPa, and the soaking delamination length decreases to 12 mm, complying with the national standard GB/T 9846—2015 Plywood for general use. The study confirms that optimized temperature and relative humidity conditions can significantly shorten the curing time of magnesium oxychloride adhesives and improve the performance of magnesium oxychloride inorganic plywood, providing key parameters for industrial production.关键词:magnesium oxychloride adhesive (MOA);inorganic plywood;curing time;518 phase2|0|0更新时间:2025-12-15
摘要:By regulating temperature and humidity conditions, the curing process of magnesium oxychloride adhesive can be optimized; the microstructure and properties of inorganic plywood can be improved as well. Plywood from Cunninghamia lanceolata veneer with magnesium oxychloride adhesive was prepared under different temperature and humidity conditions during the curing environment. The curing time, microstructure, and plywood properties of magnesium oxychloride adhesive were experimentally tested. Microscopic analysis showed that suitable temperature and humidity promotes the oriented growth of 518 phase crystals (5 Mg(OH)₂•MgCl₂•8H₂O) and inhibits the formation of Mg(OH)₂, which significantly enhance the cross-linking density of the adhesive. Under conditions of 70 °C and 30% relative humidity, the content of 518 phase crystals in the adhesive reached its peak, forming a dense and orderly microstructure inside the plywood, resulting in an increase of static bending strength to 54 MPa and an increase of elastic modulus to 7 407 MPa, which was improved by 44.8% and 39.1% compared to the control samples cured under conventional conditions; the bond strength reaches 0.98 MPa, and the soaking delamination length decreases to 12 mm, complying with the national standard GB/T 9846—2015 Plywood for general use. The study confirms that optimized temperature and relative humidity conditions can significantly shorten the curing time of magnesium oxychloride adhesives and improve the performance of magnesium oxychloride inorganic plywood, providing key parameters for industrial production.关键词:magnesium oxychloride adhesive (MOA);inorganic plywood;curing time;518 phase2|0|0更新时间:2025-12-15
RESEARCH BRIEFING
-
 摘要:With the growing personalized demand in the consumer market, the customized panel furniture industry is accelerating its transformation to small-batch and multi-variety flexible manufacturing. As the core decision-making link, workshop scheduling faces the challenges from strong process coupling, multi-objective conflicts, and frequent dynamic disturbances. Therefore, how to respond quickly and schedule reasonably to frequent dynamic events in the workshop is one of the keys to improving production efficiency. The issues in workshop scheduling of customized panel furniture are complex, which involves product production process, workshop production mode, and dynamic disturbance. The research status on scheduling methods based on efficient scheduling in customized panel furniture workshop is analyzed, including classical exact algorithm, heuristic and meta-heuristic algorithm, and machine learning. To address the challenges of scheduling method for customized panel furniture workshop based on efficient scheduling, a hierarchical collaborative scheduling framework of “prediction-response” mechanism is proposed. The framework combines static pre-scheduling optimization with dynamic real-time scheduling so that to improve the response ability of the workshop to dynamic events and provide theoretical support and practical path for the intelligent transformation of the customization panel furniture industry.关键词:customized panel furniture;intelligent algorithm;workshop scheduling;dynamic scheduling;reinforcement learning24|0|0更新时间:2025-12-15
摘要:With the growing personalized demand in the consumer market, the customized panel furniture industry is accelerating its transformation to small-batch and multi-variety flexible manufacturing. As the core decision-making link, workshop scheduling faces the challenges from strong process coupling, multi-objective conflicts, and frequent dynamic disturbances. Therefore, how to respond quickly and schedule reasonably to frequent dynamic events in the workshop is one of the keys to improving production efficiency. The issues in workshop scheduling of customized panel furniture are complex, which involves product production process, workshop production mode, and dynamic disturbance. The research status on scheduling methods based on efficient scheduling in customized panel furniture workshop is analyzed, including classical exact algorithm, heuristic and meta-heuristic algorithm, and machine learning. To address the challenges of scheduling method for customized panel furniture workshop based on efficient scheduling, a hierarchical collaborative scheduling framework of “prediction-response” mechanism is proposed. The framework combines static pre-scheduling optimization with dynamic real-time scheduling so that to improve the response ability of the workshop to dynamic events and provide theoretical support and practical path for the intelligent transformation of the customization panel furniture industry.关键词:customized panel furniture;intelligent algorithm;workshop scheduling;dynamic scheduling;reinforcement learning24|0|0更新时间:2025-12-15
DISCUSSION &SUGGESTION
- 摘要:The international standard ISO 5942:2024, Bamboo-Wood Composite for Container Flooring, was officially published in August 2024, marking the first international standardization of bamboo-based engineered material in the container manufacturing sector. This paper provides a comprehensive overview of the standard' s development background, formulation process, and technical requirements. It offers detailed interpretations of the key components, including classification, technical requirements, inspection methods, inspection rules, as well as guidelines for marking, packaging, transportation, and storage. ISO 5942:2024 emphasizes two core performance dimensions: bonding durability and loading-bearing capacity, defining critical parameters such as moisture content, density, bond durability, concentrated load, and floor strength. Specifically, the standard stipulates a minimum density of 0.75 g/cm3 and a moisture content range of 6%~12%. For bonding durability, ISO 5942:2024 differentiates between flooring with and without strands. In strand-free flooring, the total delamination length of any adhesive layer on each side must not exceed one third of the length of the adhesive layer. For strand-included floor, delamination must not exceed half of the side length, with no more than 2 points of delamination per side in the thickness direction. The concentrated load capacity requires at least 65 000 N, simulating localized pressure from forklift wheels during loading operations. Floor strength is evaluated in accordance with ISO 1496-1:2023, using a wheeled test vehicle with a 7 260 kg axle load to assess fatigue resistance under dynamic loading conditions. This paper also presents a comparative analysis of ISO 5942:2024 with China' s national standard GB/T 19536—2015 and the group standard T/CSF 009—2019, focusing on differences in dimensional specifications, appearance requirements, and physical-mechanical performance. As the first international standard for bamboo-wood composite for container flooring, ISO 5942:2024 provides a unified technical framework for facilitating global trade, while advancing the green, standardization development of the bamboo and container flooring industry. Its publication contributes to global efforts in climate change mitigation, sustainable manufacturing, and the advancement of low-carbon economies.关键词:Container flooring;international standard;bamboo-wood composite40|0|0更新时间:2025-12-15
DISCUSSION ON STANDARDS
0

